Simulation for thermal environment of facilities
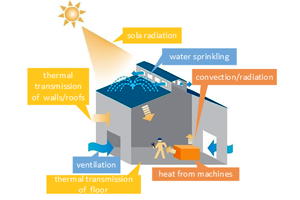
A simulation technology for estimating the temperature of large-roofed buildings, such as factories. Focusing on thermal environmental factors, we can readily predict the indoor environment of factories and similar facilities.
ECO ventilation

A system that facilitates indoor ventilation by combining cooled humidified air supply with air exhaust that use waste heat and wind power. The indoor environment can be cooled without using electricity for air conditioning or ventilation.
Air supply louvers with water

Indoor rooms are cooled by spraying mist on the outside of air supply louvers introducing air into the room. This improves indoor temperature and prevents deterioration of equipment efficiency due to heat.
Roof water sprinkling system

A roof cooling system using a mechanism that dissipates heat through water evaporation without using air conditioning. SMC develops a system that provides maximum cooling effect with the minimum amount of sprayed water, and have applied it to a large number of buildings.
Solar chimney natural ventilation system

A natural ventilation system for buildings that harnesses the temperature rise due to sunlight and air ventilation. Natural ventilation responsive to the time, wind and rain, temperature, and humidity is achieved through a built-in automated control at openings.
Displaycement ventilation system

An air conditioning system that effectively ventilates and cools the vicinity of floors where human activity is concentrated. This can efficiently perform the air conditioning of large rooms with high ceilings. In particular, when there is a heat source in the room, heat reduction is higher and ambient air cooling is easier to achieve.
